
- September 4, 2025
- Top Search
- 10:17 am
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a futuristic idea—it is reshaping the very foundations of the U.S. economy. On one hand, massive investments and stock market gains signal AI’s transformative potential. On the other, looming job losses and consumer caution raise questions about whether this growth will be sustainable. The debate has never been more pressing: Will AI drive America’s next economic boom—or slow it down?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the U.S. economy. On one hand, massive AI investments and booming tech stocks are fueling growth. On the other, rising fears of job losses are casting a shadow. The big question: Will AI be a growth engine—or a drag on the U.S. economy in 2026?
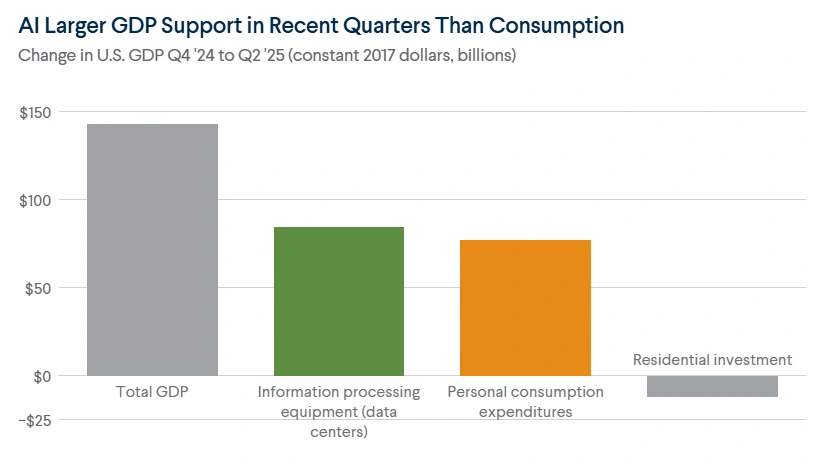
AI’s Current Contribution to U.S. Growth
1. AI Capital Expenditures: Private-Sector Stimulus
Since the launch of ChatGPT in 2022, tech giants like Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and Meta have collectively invested hundreds of billions into AI infrastructure. In 2025 alone, AI-related capital expenditures are expected to reach $361 billion, comparable to historical government stimulus packages.
Key Example: Between Q4 2024 and June 2025, AI-driven data center investments contributed more to GDP growth than consumer spending.
2. AI Wealth Creation: Boosting Consumer Confidence
The stock market has been riding the AI wave. Nvidia, Meta, and AMD soared in early 2023, while hyperscalers collectively added $10.3 trillion in market value since late 2022. This wealth effect supports consumer confidence and spending, translating into an estimated $63B–$112B boost in consumer spending.
The Risks: AI-Driven Job Losses
1. Layoffs and Workforce Shifts
While AI investments are rising, layoffs are also mounting. In 2025, over 806,000 job cuts were announced (Jan–July), with AI directly accounting for 10,375 of them. CEOs are increasingly looking to AI for cost savings, signaling more cuts ahead.
Survey Insight: According to a Conference Board survey, over one-third of CEOs expect their workforce to shrink in 2026—the first time since 2020 that cuts outpace hiring expectations.
2. Predictions from AI Leaders
Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei predicted that AI could eliminate 50% of entry-level white-collar jobs within five years, potentially driving U.S. unemployment as high as 10–20%.
3. Consumer Caution
Job losses directly affect spending. With consumption making up two-thirds of U.S. GDP, reduced incomes could drag growth below the 1.7% Bloomberg consensus forecast for 2026.
The Infrastructure Challenge: Can AI Keep Scaling?
Even with record spending, scaling AI faces limits:
Energy demand: U.S. data centers’ electricity needs jumped from 50 to 134 gigawatts in a year, outpacing utility commitments.
Costs: Rising tariffs on steel, copper, and semiconductors increase infrastructure expenses.
Inflation risk: Electricity prices rose 6.5% YoY, with data centers responsible for much of the spike.
This raises questions: Can AI’s rapid buildout continue without hitting physical and cost roadblocks?
Equity Rally: Can It Last?
The AI-fueled stock rally has been extraordinary—but how long can it continue?
Potential Risks:
Federal Reserve policy shifts: If inflation remains sticky, expected rate cuts may not materialize, pulling equities lower.
China comparison: U.S. AI progress could be judged against China’s advancements, risking investor disappointment.
Infrastructure bottlenecks: Energy shortages, raw material tariffs, and limited data center capacity may slow future AI spending.
Electricity Price Inflation: Data centers alone drove 70% of energy cost increases in parts of the U.S., pushing household prices up 6.5% (2024–2025).
Putting AI in Historical Context
AI’s economic impact is massive but not unprecedented:
Railroads (1828–1860): 2.5% of GDP
Telecom boom (2000): 1.2% of GDP
AI today (2025): 1.2% of GDP
Like past innovations, AI could fuel long-term growth—but short-term risks remain.
Policy and Market Outlook
Tariffs: Likely to offset growth benefits for most households.
Deregulation: Could lower business costs, but impact timing is unclear.
Federal Reserve Policy: Balancing inflation and employment is critical. Missteps could slow AI-driven momentum.
Political Influence: A politicized Fed could erode investor trust and drive up long-term borrowing costs.
Looking Ahead: Will AI Help or Hurt U.S. Growth?
The outlook for 2026 is mixed:
Positive: AI capital spending and wealth creation are still strong drivers of GDP.
Negative: Rising job cuts and inflation risks could weaken consumer demand.
Consensus GDP growth forecast for 2026: 1.7%—but downside risks loom.
Conclusion: A Double-Edged Sword for U.S. Growth
Artificial Intelligence is simultaneously a growth engine and a disruptor. Its capital expenditures and stock-driven wealth creation are powering today’s economy, but looming job losses and rising costs may temper tomorrow’s growth. As the U.S. heads into 2026, the question isn’t whether AI will impact growth—but whether the balance will tip more toward opportunity or risk.
FAQs
AI is boosting growth through capital spending on infrastructure and wealth creation in stock markets.
Not yet. Only 1.3% of layoffs in 2025 were AI-related, but executives predict bigger cuts soon.
They provide the computing power and storage needed to train advanced AI models.
Yes. Rising data center energy demand has already contributed to higher electricity prices.
Economists forecast 1.7% growth, but risks from job cuts and inflation could lower that figure.

Recent Posts:


AI Chatbot 2025: From ELIZA to Next-Gen Smart Assistants


